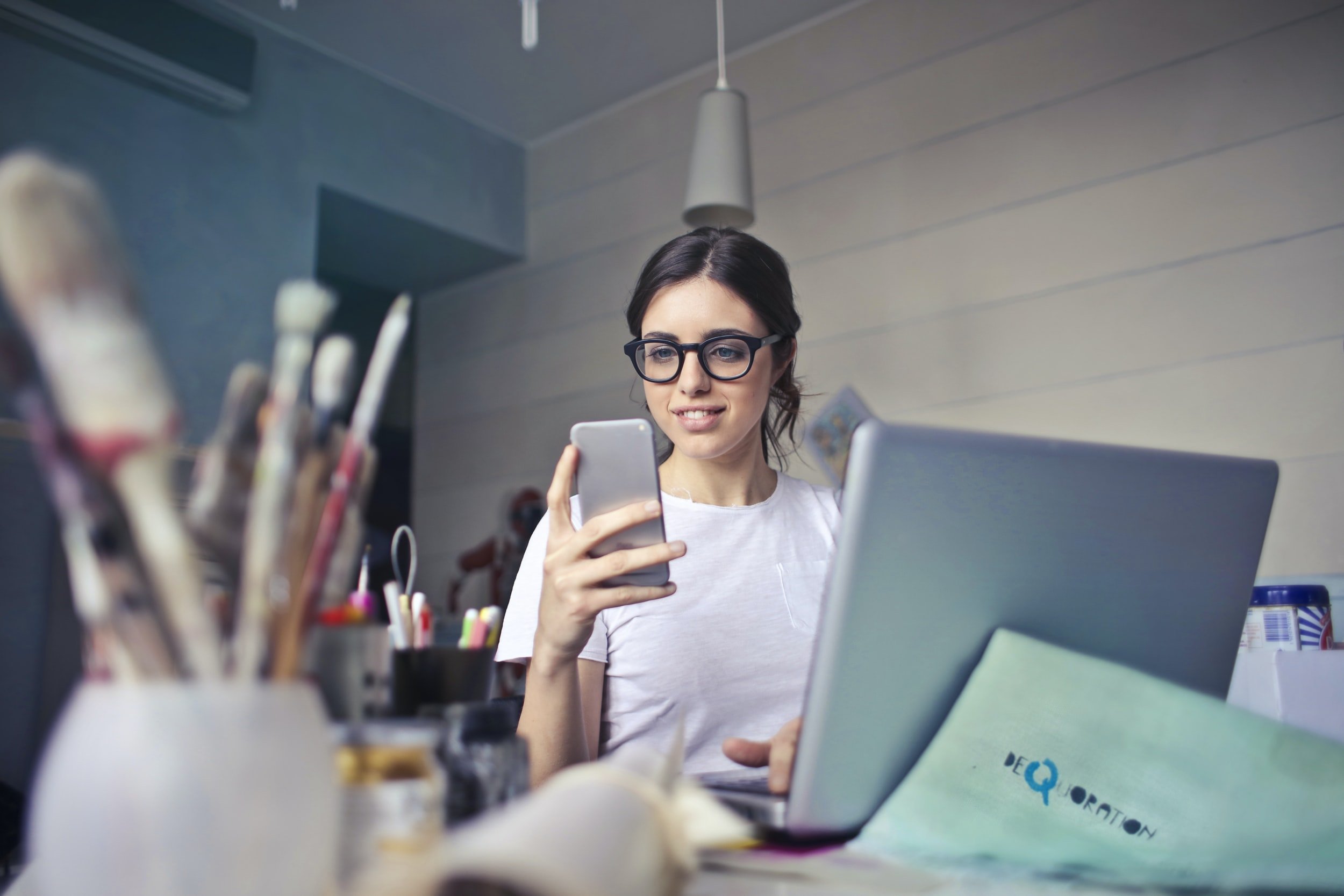
Overcome Perfectionism with Professional Counseling.
Are your perfectionist tendencies negatively impacting your life? Learn how online therapy can help you manage your perfectionism more healthily.
What is perfectionism?
Perfectionism is a personality trait characterized by high standards and a need for perfection. People who are perfectionistic often set unrealistic goals with the expectation that they will meet these impossible standards. While it is admirable to strive for excellence, perfectionism can be problematic because it is often based on unrealistic expectations. When people are unable to meet their own high standards, they may experience feelings of failure, inadequacy, and worthlessness. This type of thinking styles perpetuate negative schemas and irrational thought patterns.
How does perfectionism manifest?
Perfectionism can manifest in different ways. Some perfectionists may only have very high standards for themselves while others may have high standards for themselves and others. Perfectionists often strive for perfection in all areas and aspects of their lives. Despite the fact that there are no single causes of perfectionism. Perfectionism is developed from a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Some people may be born with a predisposition towards perfectionism, while others may develop it in response to their environment.
Perfectionistic parents or caregivers, for example, may inadvertently teach their children that only perfect behavior is acceptable. Similarly, people who live in highly competitive environments may develop perfectionism as a way to cope with the pressure to succeed. As a result, perfectionists struggle with accepting anything less than perfectionism in how they act, how they look, and what they do in order to control how others see them.
As a consequence, perfectionists are highly critical of themselves. When they do not meet their unrealistic standards, the perfectionist can become inwardly abusive to themselves. Due to their negative thinking styles and cognitive distortions. People who are perfectionists continuously feel overwhelmed and stressed even though outwardly they look like they have it all together and figured out. Until the feeling of anxiety becomes too much, perfectionists tend to have anxiety attacks or anger outburst that leads to avoidance and irrational behavior followed by a depressive episode. Perfectionism tendency can also lead to social isolation, in fear of letting others see their imperfections. They often feel they cannot ask for help due to fear of appearing weak or being rejected.
So, what is the role of anxiety in perfectionism?
Anxiety likely plays a role in both the development and maintenance of perfectionism. It is also possible that anxiety and perfectionism share a reciprocal relationship, with each condition exacerbating the other. Perfectionism can lead to anxiety because of the constant worry about not meeting one's high standards. Perfectionists often have a fear of failure, and this fear can trigger anxiety. A perfectionist's critical nature can also contribute to anxiety because they are often critical of themselves and others.
Anxiety and perfectionism often go hand in hand because they share some common features. For example, both anxiety and perfectionism involve a tendency to focus on negative outcomes, dwell on mistakes, and be overly self-critical. Furthermore, both anxiety and perfectionism can lead to avoidance behaviors. While it is perfectly normal to have high standards and to strive for excellence, perfectionism becomes problematic when it starts to interfere with your life.
So, what is the role of Depression in perfectionism?
Depression is also thought to play a role in perfectionism. As we know, perfectionists often have high standards for themselves and others, and when they are unable to meet these standards, they may feel depressed. Furthermore, perfectionistic people often ruminate on their mistakes and dwell on negative thoughts, which can lead to depression. So, it is not surprising that anxiety and depression are often comorbid with perfectionism.
Perfectionism can make you depressed in a number of ways. First, as mentioned earlier, perfectionists often have high standards for themselves and others. When they are unable to meet these standards, they may feel depressed. Second, as we know perfectionists often ruminate on their mistakes and dwell on negative thoughts. This constant focus on negative thoughts can lead to depression and the development of negative schemas. Third, perfectionists may have difficulty enjoying their accomplishments because they are never satisfied with their work. Finally, perfectionists often avoid taking risks for fear of failure. This avoidance can lead to a sense of stagnation and loneliness, which can also contribute to depression.
So, what is the role of procrastination in perfectionism?
Procrastination is often a symptom of perfectionism. Perfectionists may put off starting a task because they are afraid they will not be able to do it perfectly. They may also procrastinate finishing a task because they are never satisfied with their work. Procrastination can lead to feelings of anxiety, guilt, and shame. It can also make it difficult to meet deadlines.
So, what is the role of anger in perfectionism?
Anger is often a symptom of perfectionism. Perfectionists may get angry with themselves when they make mistakes or fail to meet their high standards. They may also get angry with others when they do not meet their expectations. Anger can lead to conflict, isolation, and anxiety. It can also make it difficult to manage stress.
Is perfectionism a trauma response?
Yes, there is a strong connection between perfectionism and trauma. Perfectionism can be seen as a way of coping with trauma, as it can be a way of trying to control one's environment and create a sense of order in an otherwise chaotic life. It can also be a way of numbing oneself to the pain of past traumas. For many people who have experienced trauma, perfectionism can be a way of seeking approval and validation from others, as well as a way of trying to avoid criticism. Perfectionism can also be a form of self-harm, as it can lead to unrealistic expectations and an unhealthy striving for perfection that is often unattainable.
There are a few key signs that may indicate that someone is struggling with perfectionism:
Setting unrealistic standards: Perfectionists often set impossibly high standards for themselves and others. They may need to be perfect in all aspects of their lives, and they may expect others to meet these same high standards.
Being overly self-critical: Perfectionists are often their own worst critics. They may be quick to point out their own mistakes and dwell on their shortcomings.
Avoiding difficult tasks: Because of their fear of failure, perfectionists may avoid challenging tasks or situations. They may procrastinate on important projects, and they may shy away from the competition.
Feeling anxious and depressed: Perfectionism can lead to anxiety and depression because of the constant worry about not meeting one's high standards. Perfectionists often have a fear of failure, and this fear can trigger anxiety. Furthermore, perfectionists are often critical of themselves and others, and this criticism can also contribute to anxiety.
If you think you might be a perfectionist, there are some things you can do to help manage your perfectionism.
First, try to identify your perfectionistic tendencies:
What are the standards that you set for yourself?
Are they realistic?
What are the consequences of not meeting these standards?
Second, try to challenge your perfectionistic thinking:
Are your high standards really necessary?
What is the worst that could happen if you made a mistake?
Would it really be the end of the world?
Lastly, try to practice self-compassion:
Be kind and understanding towards yourself.
Remember that you are human and that it is okay to make mistakes.
Set up an appointment with a professional counselor who specializes in perfectionism.
How can perfectionism be treated?
There are a number of ways to treat perfectionism. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is often used to help perfectionists challenge their negative thoughts and beliefs. CBT can also help people learn to set realistic goals and accept imperfection. Meditation and relaxation techniques may also be helpful in reducing stress and anxiety. Dialectical behavior therapy (DBT)skills training is another treatment option that can help people with perfectionism. This treatment focuses on teaching skills such as mindfulness and emotional regulation. Eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR) is a newer treatment that has shown promise in treating perfectionism. This therapy uses eye movements to help people process and release negative emotions. If you think you might be a perfectionist, it is important to seek professional help. Perfectionism can be a difficult trait to manage on your own. With treatment, you can learn to accept imperfection and live a happier, more fulfilled life.
Learn how to manage your perfectionism in a more healthy and productive way.
Perfectionism is a treatable condition, and there are many resources available to help you manage your symptoms. With treatment, you can learn how to set realistic goals, deal with failure, and enjoy your life.
Therapy Designed to Help You Heal and Step Into Your Authentic Self.
You deserve to live a life driven by your passion and purpose, not your emotions. Allow me to help you make the changes you have been longing for. It's time to move on from your past, reclaim your future and step into your authentic self. Imagine a life where you no longer feel controlled by your thoughts, where you freely express yourself with conviction, honor your body, and celebrate all its imperfections. Take your next step confidently in the direction of your dreams, and live the life you have always imagined. Take comfort in knowing that you are no longer in this alone. You are in safe experienced hands now.